close
Choose Your Site
Global
Social Media
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-05 Origin: Site









Have you ever wondered why a straw looks bent in water?That’s refraction and it’s the science behind refractometers.A refractometer is a simple tool with powerful uses.It helps measure how light bends in different substances.In this post, you’ll learn what a refractometer is, how it works, and why it matters in real life.
Ever noticed how a straw looks bent in a glass of water?
That’s not magic — it’s refraction.
Refraction happens when light changes direction.
It occurs as light moves from one material to another.
Light speeds up or slows down depending on the medium.
This causes it to bend at the boundary line.
Think air and water. Light travels faster in air, slower in water.
So, when it crosses between them, it bends. That bend is refraction.
Refractometers use this bending of light to tell us more about liquids and materials.
It tells us how much light bends in a substance.
Here's the formula:
n = c / v
n = refractive index
c = speed of light in a vacuum
v = speed of light in the substance
The higher the index, the more the light bends.
Air has an index close to 1. Water is around 1.33.
The material itself
The temperature of the sample
The wavelength of light used
For example, honey and olive oil bend light differently.
That’s how we use refractometers to identify them.
Let’s go a bit deeper — meet Snell’s Law.
It describes how light bends when it moves between two materials:
n₁ × sin(θ₁) = n₂ × sin(θ₂)
n₁, n₂ are refractive indices
θ₁, θ₂ are the angles of light
Now imagine the light hits at a steep angle.
At some point, instead of bending, it reflects.
That angle is called the critical angle.
Go past it — the light bounces back inside.
Refractometers use this point — where light flips — to get an accurate reading.
They find that line between light and dark, and calculate the index from there.
Here's a simple diagram idea to visualize:
| Light Behavior | What Happens |
|---|---|
| Below critical angle | Light bends (refracts) |
| At critical angle | Light travels along the boundary |
| Above critical angle | Light reflects (no refraction) |
This is how light helps us read the invisible — with science and a bit of glass.
Let’s open up a refractometer — here’s what’s inside:
The Prism
This is where the magic starts.
You place the liquid sample directly on it.
It touches the light and helps bend it.
Light Source
Natural light works for handheld models.
Digital types use LEDs to shine through the sample.
Light enters the sample through or under the prism.
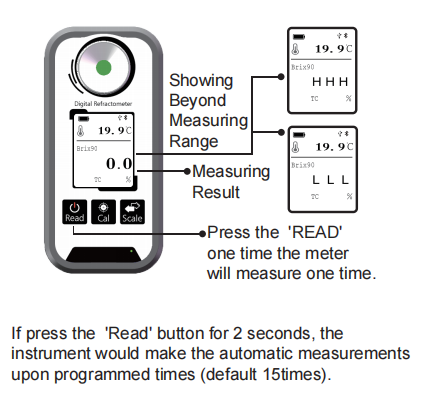
Viewing Scale or Digital Display
Analog refractometers have a scale you read through a lens.
Digital ones show numbers on a screen, automatically calculated.
Step 1: Place the Sample
Just a few drops — 2 to 5 is enough.
Spread it gently over the prism surface.
Step 2: Light Travels Through the Sample
The light passes into the sample.
It bends depending on the solution’s density.
Step 3: Measure the Angle of Refraction
The device captures the point where light shifts —
That’s the “critical angle.” It’s key to calculating the refractive index.
Step 4: Read the Result
Analog devices: Look into the eyepiece, find the line where blue meets white.
Digital devices: The screen shows you the number — simple and fast.
Light bends differently at different temperatures.
Warm samples may give lower readings than cold ones.
Even the prism itself expands slightly with heat.
So, temperature control is a big deal.
Automatic Temperature Compensation (ATC) adjusts for temperature changes.
It’s built into most digital and some analog refractometers.
ATC ensures accurate readings — whether it’s hot or cold.
You’ll need a reference liquid — usually distilled water or a known oil.
Steps to calibrate (analog version):
Clean the prism.
Add 1–2 drops of the reference liquid.
Look into the eyepiece.
Turn the calibration screw until the line hits zero or the correct value.
Repeat often — especially if the tool hasn’t been used in a while.
Here's a quick table:
| Calibration Item | Common Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Distilled Water | 0.0° Brix | Room temperature |
| Olive Oil | ~71.5° Brix | For honey refractometers |
| Liquid Paraffin | ~24.5% water | Used in moisture scale setups |
That’s how refractometers stay reliable — even after many uses.

Refractometers come in many styles.
Each one fits different users — from winemakers to engineers.
These are the most common type.
You can hold one in your hand and use it almost anywhere.
Analog models use natural light and an eyepiece.
You read a scale manually.
Digital versions use LED lights and sensors.
Results show instantly on a screen.
| Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Analog | Low cost, no batteries, field-ready | Needs calibration, less precise |
| Digital | Fast, accurate, easy to read | More expensive, needs power |
Winemakers check grape sugar levels (Brix).
Beekeepers test honey moisture.
Aquarists measure saltwater salinity.
These are large, bench-top devices.
Named after Ernst Abbe, who invented them in 1869.
They use two prisms — one smooth, one rough — for spreading and measuring light.
Users rotate them to align the light/dark boundary in the viewer.
Abbe refractometers are perfect for:
Labs and universities
Testing solids or viscous liquids
High-precision research
They’re not portable but very accurate.
These devices use LED light sources and image sensors.
Light bends through the sample, then hits a detector.
A chip measures the angle and converts it to a digital value.
Manual digital: You drop the sample, press a button, get a number.
Automatic: Built for labs — some models even clean themselves.
They’re used in food labs, research centers, and quality control rooms.
These aren’t handheld at all.
They’re installed directly in pipes or tanks in factories.
Inline refractometers measure solutions as they flow — no need to stop production.
They:
Help control product quality
Provide real-time feedback
Handle harsh industrial environments
Used in:
Food and beverage factories
Chemical plants
Oil refining lines
Some refractometers do just one job — really well.
They measure sugar content in liquids.
Used in:
Juice testing
Wine production
Honey quality checks
These measure salt concentration.
Units may show:
Parts per thousand (ppt)
Percentage (%)
Permille (‰)
Helpful for:
Brine making
Seafood processing
Aquariums
Gem refractometers identify stones by optical properties.
Automotive refractometers test antifreeze and battery fluids.
Each one is tuned for a specific job — using the same light-bending magic.
Refractometers aren’t just for labs.
They’re everywhere — from farms to food factories.
Food makers use refractometers to check quality and flavor.
They help ensure every batch meets the right sweetness or thickness.
The Brix scale shows how much sugar is in a liquid.
1° Brix = 1 gram of sugar per 100g solution.
| Product | Typical Brix Range |
|---|---|
| Grape Juice | 14–19° Brix |
| Honey | 70–88° Brix |
| Jams & Jellies | 60–70° Brix |
| Juices | 10–20° Brix |
Wine: Measure sugar before and during fermentation
Fruit juice: Check sweetness and shelf stability
Honey: Ensure moisture is low enough to prevent fermentation
Dairy: Confirm solids and fat levels in milk or yogurt
Farmers and beekeepers rely on quick readings.
Beekeepers test honey moisture — must stay below 18%
Growers check fruit ripeness by sugar level
Crop monitors use readings to decide harvest timing
A handheld refractometer helps them do all this on the field — fast and easy.
Labs use refractometers to analyze what’s inside a liquid.
They check the chemical makeup of samples
They help identify unknown substances by comparing refractive index
It’s a fast method, especially for mixtures with sugar, salt, or alcohol.
Used in:
Food science
Chemistry
Biotech research
Refractometers support production lines across industries.
Fluid concentration (e.g., cutting oils, coolants)
Mix validation — is the blend right?
Process control — maintain product specs
| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| Beverage | Juice concentration tracking |
| Chemical | Mixing solvents, acids, alcohols |
| Paint & Coating | Monitoring resin levels |
| Lubricant | Testing water/oil separation |
Inline models read values without stopping the process.
Gemologists use special refractometers.
They shine light into gems and check how much it bends.
Each gem has a unique index.
If the number matches, it confirms the type.
Auto shops use refractometers to test:
Coolant concentration
Battery fluid density
Windshield washer fluids
It’s quick, clean, and helps prevent engine trouble.
Using a refractometer is simple — if you follow a few key steps.
Let’s walk through setup, measurement, and best practices.
Before anything, you need to calibrate your device.
This ensures the readings are accurate — every time.
Analog Models:
Clean the prism with a soft, lint-free cloth.
Add 1–2 drops of calibration fluid (like distilled water).
Close the cover plate.
Look through the eyepiece and turn the calibration screw.
Align the reading to 0.0 or the known Brix value.
Digital Models:
Use the "zero" function with distilled water.
Follow on-screen instructions to calibrate using a reference liquid.
Some models auto-adjust for temperature.
Pick a fluid that matches your device’s range.
| Reference Fluid | Brix Value / Water % | Usage Example |
|---|---|---|
| Distilled Water | 0.0° Brix | General calibration |
| Olive Oil | ~71.5° Brix | Honey refractometers |
| Liquid Paraffin | ~24.5% water content | Moisture scale calibration |
Mark the bottle so you don’t forget its values.
Now it’s time to test your sample.
Just 2–5 drops is enough.
Too much might spill; too little won’t cover the prism.
Analog: Hold the device toward a bright light source.
Natural light or a lamp works best.
Digital: Internal LED light handles this for you.
Analog: You’ll see a blue and white field.
The line where they meet shows the value.
Digital: The screen shows exact numbers.
Many also display temperature and unit type.
Always wipe the prism clean before and after each use.
Use a damp, soft cloth — no paper towels.
For better accuracy:
Stir thick samples like honey first.
Take 3 readings and average the result.
Write down:
The Brix or moisture value
The sample name
The date and time
The temperature if not using ATC
Here’s a sample log:
| Sample | Reading | Unit | Temp (°C) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grape juice | 16.2 | Brix | 25 | First press batch |
| Honey | 17.8 | %Water | 20 | Summer harvest |
| Coolant | 38.5 | % | 23 | Needs dilution |
Different refractometers show results in different ways.
Let’s break down the most common scales.
The Brix scale is all about sugar.
It tells you how much sugar is in a liquid — in percentage.
1° Brix = 1 gram of sugar in 100g solution
The Brix scale was created for measuring sugar in wine and fruit juice.
Now, it’s used in honey, soda, jelly — even tomatoes.
If your juice reads 15° Brix, it contains 15% sugar by weight.
The higher the Brix, the sweeter and denser the liquid.
| Brix (%) | Approx. Sugar (g/100ml) | Example Product |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | 5 | Sports drinks |
| 12 | 12 | Orange juice |
| 18 | 18 | Ripe grapes |
| 70–88 | 70–88 | Honey |
Not every liquid is sweet.
So, other scales were made for other tasks.
Used in brewing beer.
It measures sugar plus other solids in wort (unfermented beer).
Similar to Brix, but includes proteins, minerals, etc.
Baumé is used for salty or heavy liquids.
Two scales: one for liquids heavier than water, one for lighter
Originated from salt solutions like brines
This one’s just for grape must (fresh juice from grapes).
1° Oechsle = 1g more per liter than pure water
More °Oe = more sugar = stronger wine later.
Salt content shows up in:
ppt: parts per thousand
%: percent
‰: permille
Used for:
Aquariums
Seaweed brine
Pickled products
Choosing a refractometer?
Here’s what to think about:
| Application | Best Refractometer Type |
|---|---|
| Wine or Juice | Brix refractometer |
| Honey Moisture | Moisture-content model |
| Beer Wort | Plato scale |
| Lab Testing | Digital or Abbe refractometer |
| Industrial Fluids | Inline refractometer |
Field testing: Handheld models are good enough
Precise lab work: Go with digital or Abbe models
Process control: Inline models give real-time feedback
| Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Analog | Cheap, no batteries needed | Manual reading, less accurate |
| Digital | Fast, clear, easy to use | Needs power, costs more |
| Abbe | Highly accurate, lab standard | Bulky, not portable |
Make sure the scale fits your task (Brix, °P, %, etc.)
Look for ATC (Automatic Temperature Compensation)
Choose models that are easy to calibrate
Check if it includes reference fluid
Buy smart — and your refractometer will serve you well for years.
Refractometers help us measure how light bends in a liquid.
They show sugar, salt, or moisture levels quickly and clearly.
You’ll find them in kitchens, labs, farms, and factories.
They make quality control easier — and faster.
Whether you're brewing beer or testing honey, a refractometer gives reliable answers.
They're simple to use, but very powerful.
Pick the right type, keep it clean, and calibrate often.
That’s the secret to accurate readings every time.
A: It measures the refractive index to determine concentration, purity, or sugar/salt/moisture levels in a solution.
A: Yes. There are specialized refractometers for honey, wine (Brix), and automotive fluids like coolant and battery acid.
A: Calibrate before each use or after long storage, especially if accuracy is critical.
A: Yes. Temperature changes light bending, which affects accuracy.
A: ATC stands for Automatic Temperature Compensation. It adjusts readings to correct for temperature effects.